Golden Rules of Accounting- Rules of Debit and Credit Explained
Hey Guys, so today we will study the most important and interesting
topic of Accounts. Golden Rules of Accounting- Rules of Debit and
Credit which is the base of accounts and the language of accounts. Under double
entry system of Book keeping each transactions has two aspects. One is called
debit and another is credit where, debit records incoming or receiving aspect
and credit records outgoing or giving aspect.
Meaning of an Account
Account is a summarised record of transactions at one place related to
the particular head. Account is prepared for sort and store the transactions.
Each individual account is stored in the general ledger and used to prepare the
financial statements at the end of the accounting period. An Account shows
specific assets, liability, revenues, assets, equity.
An Account is divided into two parts which is known as Debit and Credit,
Debit and Credit are two opposing terms. Dr. is used for
Debit and Cr. stands for Credit, Debit refers to the
left side of an account and credit refers to the right side of an account. An
item recorded on the debit side of an account is said to be debited to the
account and when an item is recorded on the credit side of an account it is
said to be credited to the account. Debit and Credit are simply additions to or
subtractions from an account. An Account is usually in a "T" shaped
layout in which both Debit and credit aspects are recorded, let's have a look
below on how an account looks-
Debit and Credit
As
we know, Under Double Entry System of Book Keeping we records both the aspects of
any financial transaction. So, at the time of recording the transaction, it is
recorded once on a credit side and again on the credit side. A Double entry
system will maintain complete records and also gives proper financial results. Debit
aspect used for receiving or incoming aspect and credit aspect is used for
giving and outgoing aspect. Debit and Credit aspects of a transaction form the
basis of Double Entry System. We know this equation which is known as an
Accounting Equation:
Assets = Liabilities
+ Capital
👉Also Read International Financial Reporting Standards(IFRS) Explained
In the Dual aspect system of Accounting we get to
know that if there is any change on one side of the above equation, there will
be a change of similar amount on the other side of the equation or among the
items comprised in the same side of the equation. To get more information on
this, hit on the link Accounting Equation.
Debiting and crediting an account- we either debit
an account or credit an account in relation to an accounting transaction. Debit
and Credit are two actions that are opposite in nature, both debit and
credit may represent either increase or decrease depending upon the nature of
the account.
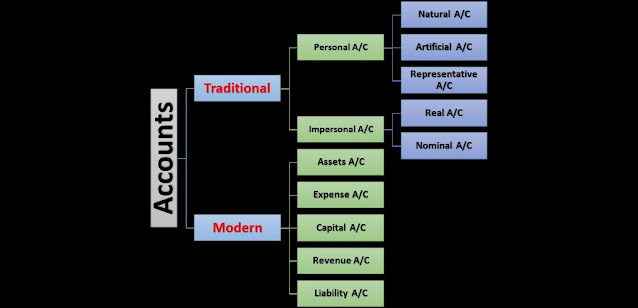
Classification of Accounts
The below image help us to show the various
accounts classified according to their nature-
In the above image we get to know that there are
namely two types of approaches in accounts, one is from the view of
Traditional approach and another is from Modern approach. Traditional approach
classified into two accounts Personal account and Impersonal account, where
Personal account further holds three types of accounts(Natural account,
Artificial account and Representative account) and Impersonal account holds two
type of accounts(Real accounts and Nominal accounts) As per Modern
approach five type of accounts are prepared(Assets Account, Expense account,
Capital account, Revenue account and Liabilities account). Let we discuss all
these accounts one by one in detail.
Traditional Classification of Accounts
Personal Accounts
As the name suggests, these accounts are related
with Persons i.e, Individuals, drawings, companies, firms, debtors, creditors
etc. Examples of some personal accounts are account of Sohan Enterprises(a good
supplier), account of M/s salvy & co.(a credit customer). The purpose of
preparing these type of accounts is to ascertain the remaining balance due from
persons and orgainizations which are related to the business transactions.
Natural Personal Accounts- These accounts are related with natural persons, it
means persons which are creations of God, Like Rakesh's Account, Manoj's
Account, etc.
Artificial Personal Accounts- These accounts do not have a physical existence as
Natural Personal Accounts, they are recognized as persons in business in
business dealings. These are known as legal entities create by humans, for
example an account of a private limited company, a society, a
trust etc.
Representative Personal Accounts- Representative Personal accounts are those accounts
which which represent certain person or group of peoples. For example salaries
due to the employees, then outstanding salary account will be opened in the
books of accounts. The outstanding salary account shows that the amount of
salary payable to the employees.
Impersonal Accounts
Any account other than personal account such as
Furniture account, Electricity Bill account, cash account etc are termed as
Impersonal accounts.
Real Accounts- The accounts which are related to tangible or
intangible assets of the firm other than any person(debtor) is known as Real
accounts. For Example- Machinery, Furniture, Land, Goodwill, Trademark etc.
Nominal Accounts- Nominal accounts are associated with Income,
Expenses, Profits and Losses. The net result of all the nominal accounts is
profit or loss which is transferred to the capital account. Example of some
Nominal accounts are- Salary account, Sales account, Purchase account, Interest
paid account etc.
Modern Classification of Accounts
Assets Account- These
accounts are associated with account of assets and properties owned by the
company such as Machinery account, Plant account, Building account, Patents
account etc
Expense Account- The money
spent in the course of business or even lost while performing the business operations
are recorded under this account.For Example- Depreciation account, Rent
account, Staff welfare account etc
Capital Account- This is
related with the accounts of the owner(Proprietor/Partners) of the business who
invested money into the business. These accounts are Capital account of owner,
Capital account of partners, Drawings account etc.
Revenue Account- When a company
earns from the sale of their operations, then revenue is generated. Under
revenue accounts Income and gains of the business are recorded, like Sales,
interest received, Discount received etc.
Liability Account- These
accounts are that of in which company records its debts from lenders, Creditors
for goods, Outstanding payment for various expenses etc.
Golden Rules of Accounting
Accounting rules guide us how to record the
transactions in the books of accounts under Double Entry System of Accounting.
Accounting rules works as a base for any accounting framework. Accounting rules
are used uniformly by all entities to reach at the consistent and comparable
Financial Statements. Golden rules of accounting are the basic accounting rules
on the basis of which accounting entries are recorded.
👉Also Read Accounting Information System Explained
👉Also Read Cash and Accrual Basis of Accounting
Real Accounts
The rule related to real accounts states Debit is
what comes into the business and credit is what goes out from the business. It
means, if something comes into the business then it would be debited in the
books of accounts and if something goes out of business, it will be credited in
the books of accounts while recording.
For Example- A Machinery was purchased by Suhana Enterprises
in cash of Rs 8500/-. Now machinery is an asset and it comes into the business
and cash was paid on behalf of Machinery. So, as per real account, the
Machinery account was debited and Cash account was credited.
Journal Entry in the books of Suhana Enterprises-
Machinery Account
...Dr 8500
To
Cash Account
8500
Personal Accounts
The rule related to Personal
Account states Debit is the receiver and credit is the giver or say, if a
person receives something into the business, then receiver's account should be
debited and if a Person gives something in the business, then giver's account
shall be credited.
For Example- Mohit receives cash of Rs 15000/- from
Sohan for his pendings. In the books of Sohan, Mohit is the receiver of that
amount and Sohan is the giver. So, Mohit's account shall be debited and Sohan's
account shall be credited with cash.
Journal Entry in the books of Sohan-
Mohit's Account
..Dr 15000
To Cash
Account 15000
Nominal Accounts
The rule related to nominal account states that all
expenses and losses of the business are debited and all income and gains of the
business are credited.
For Example- ABC Ltd. paid salaries to their staff
Rs 1Lakh, then salary is an expense it should be debited. Discount received by
ABC Ltd. of Rs 15200/- is an income so it should be credited in the books of
accounts of ABC Ltd.
Journal Entry in the books of ABC Ltd.
Salary Account
..Dr 1,00,000
To
Cash/Bank Account
1,00,000
Cash/Bank Account ...Dr
15,200
To Discount Received Account
15,200
I hope guys you all understand the topic
of Golden Rules of Accounting- Rules of Debit and Credit which is the most
important topic of Accounting and interesting although. If you have any
questions or doubts regarding this post, then please tell me in the comment
section. Thanks for reading, have a nice day.





Comments
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box